By Alyssa Cawley Gonzalez, TechChange Digital Health Program Lead
I’ve facilitated many deliveries of the Digital Health: Planning National Systems (DH:PNS) course since its creation in 2020, from fully synchronous to blended, from Chile to Egypt. But up until last month, I’d never had the privilege of seeing DH:PNS alumni connect in-person to share their digital health experiences.
GDHF 2024 featured first-ever in-person DH:PNS Alumni Event
The Global Digital Health Forum is the world’s largest and most inclusive digital health event, a major relationship- and skill-building opportunity for implementers, vendors, donors, researchers and more. This hybrid conference is planned and delivered every year by TechChange in partnership with the Global Digital Health Network and a plethora of supportive sponsors. Among those is the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), who also sponsors our DH:PNS course and the virtual Community of Practice (CoP) that keeps alumni connected long after they’ve completed their coursework.
So it only made sense to utilize GDHF to convene our DH:PNS alumni and give them the chance to connect in real life. With USAID’s generous sponsorship, TechChange planned the first-ever in-person DH:PNS Alumni Event.
Alumni found common ground and shared experiences through game-based play
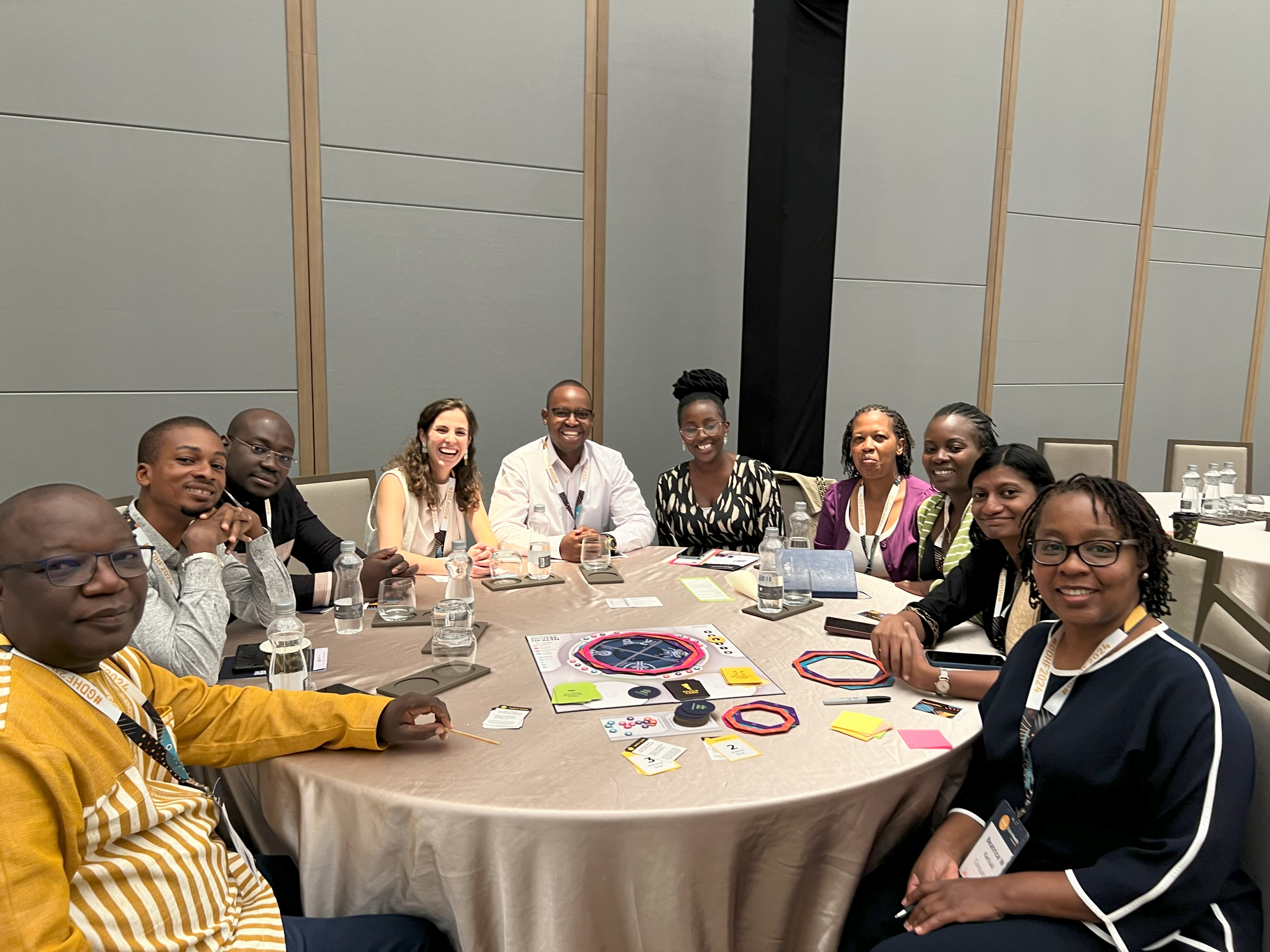
After reaching out through the CoP, TechChange convened a group of alumni who were attending the conference in a special side event to conclude the second day of GDHF. The event was designed to offer alumni and trainers the chance to network and share knowledge in an informal setting with tea, snacks, and round tables.
The event kicked off with a digital health icebreaker, where participants introduced themselves and discussed their work. Alongside the TechChange team, Merrick Schaefer, Director of USAID’s Center for Innovation and Impact (CII) in the Global Health Bureau at USAID and the funder of this initiative, gave brief opening remarks to welcome attendees.
Next, attendees split into two groups to play the Architects of Digital Health board game, discussing lessons learned from the game and their own country contexts. It was incredible to see people in person that I had gotten to know through months of online learning, and to watch them organically share their experiences dealing with concepts covered by the game in real life– crucial concepts like interoperability, the enterprise planning approach, and addressing health system challenges.dealing with shocks, and enterprise planning.
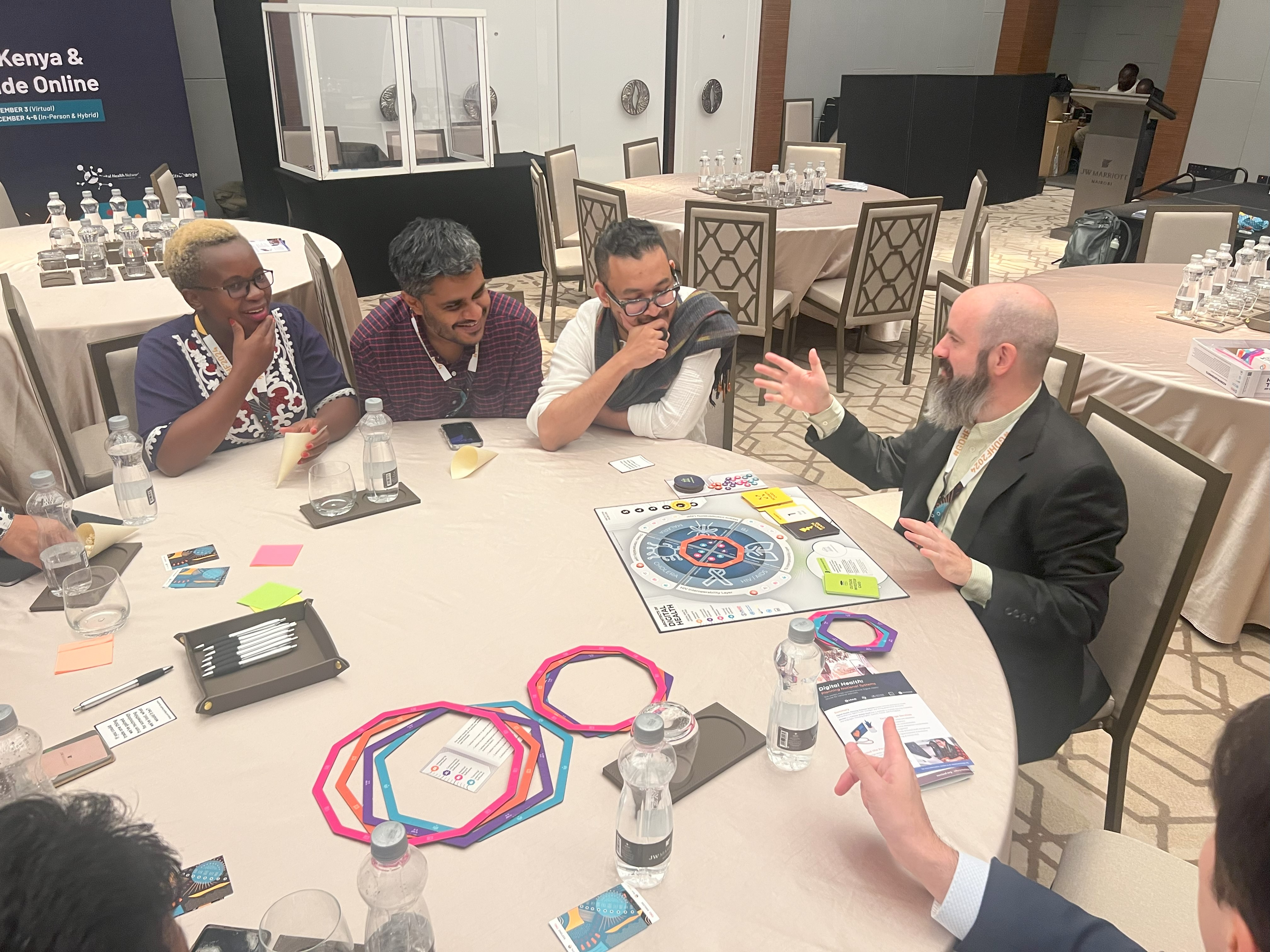

Both teams “won” in about 40 minutes, offering valuable insights on digital health initiatives.
Throughout the session, attendees also contributed ideas for future CoP activities on an “Asks and Offers” board. Common requests included live sessions for new modules and a contextualized version of the game. TechChange offered to share new modules and explore more networking opportunities in the future, given that attendees were so excited to see each other in person and build their relationships further.
For participants, the Alumni Event crystallized concepts and relationships
But don’t just take it from me that the Alumni Event was helpful and inspiring–I’m a bit biased! Our alumni took to social media to share their delight and learning experiences from connecting with their fellow alumni at GDHF.
Dr. Beatrice (Wangechi) Kariuki, an Associate Director of Data Analytics from Palladium, reflected on LinkedIn that understanding interoperability in the digital health space has stuck with her thanks to the boardgame. She shared that when she reflected on her experiences at GDHF three weeks later, the top of mind take-away for her was what it means and takes to implement interoperability in the digital health space, specifically noting “the power of games as a tool for experiential learning, [that allow] us to visualize things that are usually invisible… in a safe space where players can change their mind and strategy without impact.”
Shakira Irfaan from the Ministry of Health in Sri Lanka said that “the networking opportunity was just as valuable as the learning experience. It was a pleasure to reconnect with global experts, meet old friends, and make new connections.” PityFaith Nyokabi, an Operations Manager from Kenya added that while GDHF as a whole left a lasting impact on her digital health professional journey, it was even more special since she got “to connect in person with my fellow Digital Health: Planning National Systems course alumni and trainers…and play a more advanced version of the board game Architects of Digital Health.”
Staying connected in the future
The robust and vibrant alumni network of DH:PNS is one of the most special aspects of the course. More than 1000 people from over 90 countries have completed the course, and they work as national planners, funders, implementers and more. They are practitioners and providers, all of whom share a common passion: harnessing the power of digital health to improve health systems and health outcomes for people all over the world.
And it was amazing to see just a small group of them in-person. Our digital health team is eagerly exploring new ways to convene and connect this vibrant community in the future.
Interested in joining a future cohort or learning more about the course? Check out digitalhealthtraining.org to join the movement.