By Timo Luege, TC103: Tech Tools and Skills for Emergency Management facilitator
Working in humanitarian aid and disaster relief across several countries, I first joined the TechChange community as a student in the Tech Tools and Skills for Emergency Management online course in January 2012, and will soon be guiding discussions as a facilitator for the next round of the course that begins March 17, 2014. Since TechChange has offered this emergency management course six times since 2011, I’ve enjoyed stepping up my participation from student, to guest speaker, tech simulation demonstrator, to now a facilitator.
In my opinion, disaster management is a field where nobody is really an expert in that different people have varied areas of expertise. A facilitated TechChange course like TC103 is an opportunity to get people of different backgrounds together, which is especially valuable in a field like disaster management, which evolves so quickly and can be tough to keep track of.
Here are five lessons I have learned over the course of seven years of working in disaster response across Haiti, Liberia, Myanmar, Mali, and most recently the Philippines:

During radio programmes like this in the Philippines, disaster responders explained what assistance the survivors could expect in the aftermath of Typhoon Haiyan. Listeners submitted questions by SMS and via Facebook. Photo credit: Timo Luege
1. Build relationships early
Emergencies are not the right time for experiments. In the first phase of an emergency, disaster responders easily work 16 hours per day, seven days a week. This is not the right time to introduce new tools, unless they are an immediate time saver. If you are a technology firm, try to build relations with organizations before the next big disaster. Three months after the onset of a disaster can also be a good time to make contact, because at that stage, people have a little time to breathe but the needs are still huge.
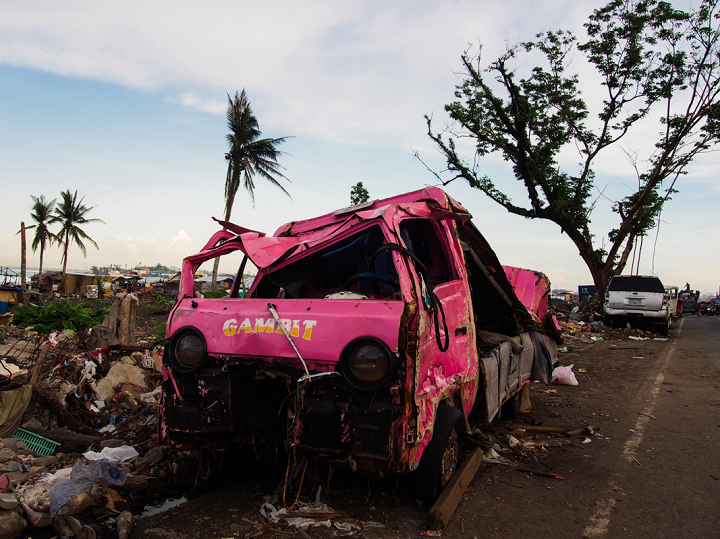

Typhoon Haiyan was deadly in two ways: what the wind couldn’t destroy, the storm surge would flatten. Along the coast houses many houses were completely pulverized and cars thrown around like toys. Photo credit: Timo Luege
2. Buy smartphones for your staff
Smartphones are amazing mobile tools that can do everything from taking photos to replacing paper forms to saving GPS information; however, many organizations still shy away from putting them into the hands of their staff. A basic, but functional, unlocked Android smartphone costs less than $80 USD in some of the more disaster prone parts of the world, and will save you many times that amount of money in gained productivity. Just think of all the paperforms you don’t have to manually enter.
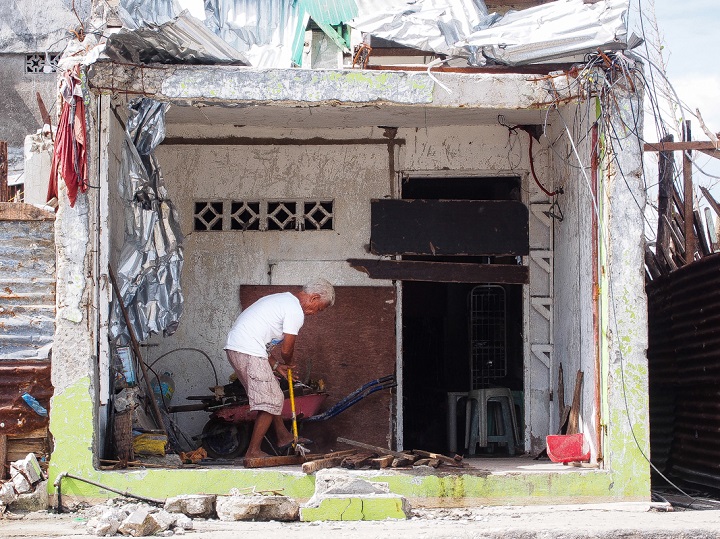

Survivors tried to salvage as many building materials as possible, including wood, corrugated iron sheeting and even nails so that they could repair their homes as quickly as possible. Photo credit: Timo Luege
3. Use tools that the affected population is familiar with
Information is critical for disaster affected people and they are eager to hear what is going on – even if it is bad news. Don’t try to impose your technology of choice on the affected people – find out what works for them. In one country it might be SMS, in another Facebook and in a third it will be old fashioned radio broadcasts or a combination of the above. As an organization, when designing your programmes, don’t focus on the tools but on what you want to achieve.
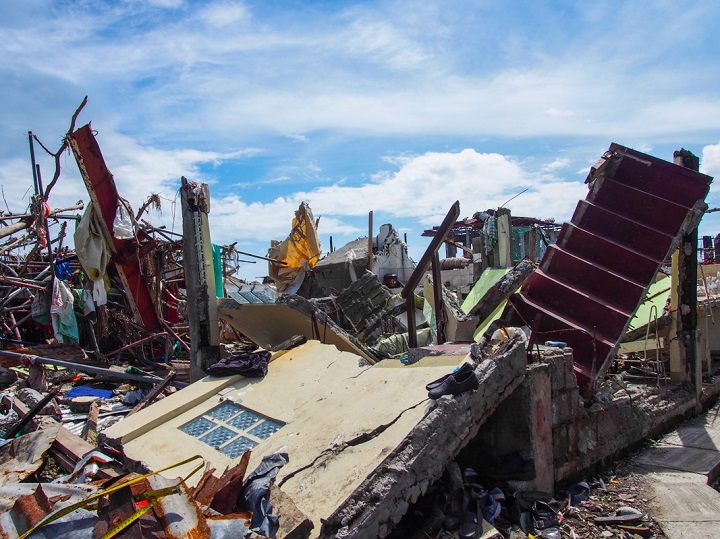

Even concrete houses like this could not withstand the force of the storm surge and were completely annihilated. Typhoon Haiyan damaged or destroyed close to 1.1 million homes. Photo credit: Timo Luege
4. Make sure the tools you use work offline
Even in a country like the Philippines, where the infrastructure is comparatively good, access to the web will be spotty, particularly after a big disaster like the recent Typhoon Haiyan. Apps and browser-based tools that require you to save information online will only frustrate you. Make sure that whatever tool you are planning to use allows you to save information offline and synchronize later.

In Tacloban, a number of large ships were washed ashore by the typhoon. The survivors used the generators on some of these boats to supply them with electricity. Photo credit: Timo Luege
5. Learn Excel
While many new technologies are more sexy and exciting, Excel is the universal language of data during an emergency. Everybody is using it. The more you know about Excel and the better you are able to import data coming from Excel files, the more information you will be able to access, process and analyze and the better your understanding of the situation will be.
Have you worked in emergency management? What are tech tools that you found useful during that disaster?
—
Interested in learning more? Enroll now in the Tech Tools & Skills for Emergency Management online course, which runs November 24 – December 19, 2014.
About the TC103 facilitator: Timo Luege
After nearly ten years of working as a journalist (online, print and radio), Timo worked four years as a Senior Communications Officer for the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) in Geneva and Haiti. During this time he also launched the IFRC’s social media activities and wrote the IFRC social media staff guidelines. He then worked as Protection Delegate for International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) in Liberia before starting to work as a consultant. His clients include UN agencies and NGOs. Among other things, he wrote the UNICEF “Social Media in Emergency Guidelines” and contributed to UNOCHA’s “Humanitarianism in the Network Age”. Over the last year, Timo advised UNHCR- and IFRC-led Shelter Clusters in Myanmar, Mali and most recently the Philippines on Communication and Advocacy. He blogs at Social Media for Good.