After a study-abroad semester in Spain and a summer at TechChange in Washington D.C., Emily Fruchterman is heading back to William & Mary to finish the final year of her undergraduate career. Before heading to Williamsburg to finish her Biology degree, she looks back on her summer internship at TechChange as an educational technologist.
1. How did you hear about TechChange?
At the start of 2014, summer internships were the last thing on my mind. I was off to spend the semester in Seville, Spain, and any thought relating to life-after-study-abroad was a painful reminder that my time in paradise wouldn’t last forever.
When my final exams forced me to face reality, I wasn’t quite sure where to start my search (the ocean between me and potential employers seemed pretty daunting). A friend referred me to internships.com, where I found out about TechChange.
2. Why did you choose TechChange to spend the summer between your junior and senior years?
TechChange piqued my interest with its goal of using the power of technology to advance social change. The broad range of courses that demonstrate the utility of technology to a very international audience showed me that this was more than a cursory commitment. Contributing to an organization with such goals seemed like a worthwhile way to spend the summer.
On a personal level, TechChange seemed like a great complement to many of my previous experiences at nonprofits and NGOs doing research while giving me new exposure to a startup culture. TechChange’s upcoming projects also aligned well with my interest in public health, plus the networking opportunities afforded by spending a summer in DC seemed too good to pass up.
3. What are your interests?
While I’m generally interested in the field of development, my passions really lie with public health. I’d really like to work for organizations (like TechChange) that have projects relating to the various aspects of health and healthcare – although my dream is to work for an organization that coordinates healthcare responses and works to improve health outcomes on an international basis. I’m also an avid coffee drinker, science fiction fan, and aspiring flamenco dancer (my time in Spain might have influenced this last one).
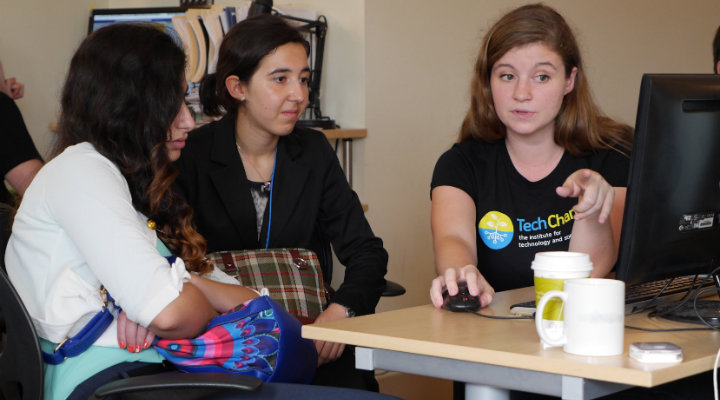

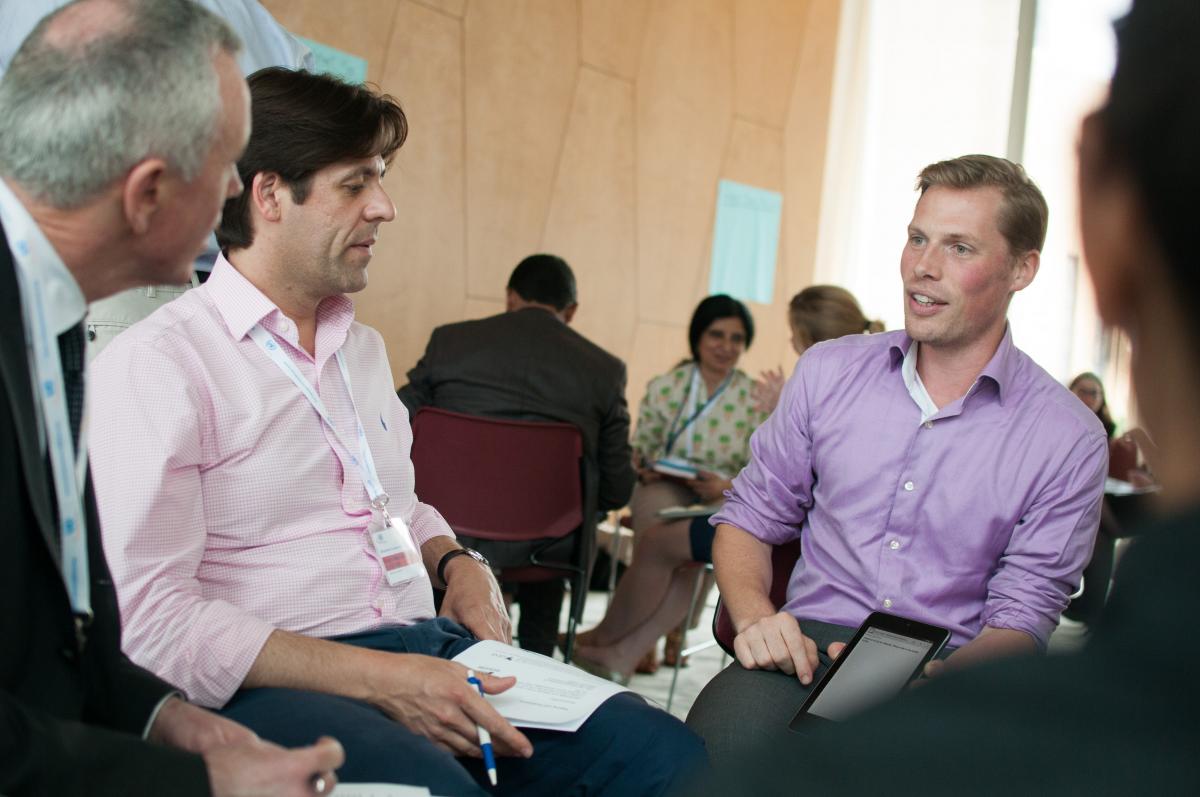
Emily goes over how to create an online course with the TechGirls on TechGirls Job Shadow Day
4. How did you use your TechChange internship to explore your interests?
Fortunately for me, TechChange had several different public health related courses this summer. I was able to engage with a course on Malaria, for use in Nigeria and Uganda, as well as take on a large part of a facilitated course on HIV for clinical and non-clinical care providers. Both of these have been extremely valuable experiences, as I’ve not only learned a great deal about both illnesses, but also looked at how to structure health-related interventions and training programs.
5. What did you do at TechChange this summer? What was your role at TechChange?
The instructional design team was finishing up a self-paced course on Malaria when I arrived in June. I was not only able to help with edits and testing, but built a few interactive elements. I got more experience building out lessons, writing storyboards, and coming up with engaging lessons while working on other instructional design projects.
I got my first taste of the facilitated platform as a teaching assistant (TA) for a course on Social Media for Social Change, during which I familiarized myself with WordPress and the structure/pacing of a four-week course. This came in super handy, as a couple weeks later I started to manage content development and build out the four modules for the course on HIV treatment. I also helped write several blog posts relating to projects, participated in meetings with clients, and taught the TechGirls from Tunisia and the Palestinian Territories how to create online courses.
6. What did you learn during your time at TechChange?
The first big thing I learned was how to use Articulate Storyline. This eLearning program might look like a fancier version of PowerPoint, but it has it’s tricks and idiosyncrasies. It was very cool to learn how to create interactions, design variables, and troubleshoot glitches to develop quality modules. This was super useful, as it helped me think about learning in a much more user-centered way.
I also learned to be much more comfortable in front of the camera – while I still had my fair share of outtakes, it became a lot easier to speak to a blinking red light instead of an audience. I learned how to manage time during interviews, ask the right kinds of questions, and (most importantly) what to do with my face when I wasn’t the one talking.
My tech skills also improved – my co workers tried to show me some coding basics (parts of which I picked up on better than others), I increased my audio editing abilities, became super familiar with WordPress, created several graphics, and set-up and took down AV equipment.
I also improved my communication skills by working closely with various members of the team on different projects and writing emails/participating in phone calls with clients.
Emily in the recording studio at TechChange before recording a live session for a course
7. Did your TechChange experience end up going as you expected?
In some ways – based on my impressions of TechChange from their website and my interview, I’d expected to find a group of young and tech savvy individuals interested in promoting social change.
I hadn’t expected how much support they’d give me for pursuing my own ideas from the get-go. I think it was my second or third day here that I suggested an interaction be added to a part of a self-paced course to a member of the instructional design team. The response I received – “great, want to build it?” – really surprised me. I’d barely started learning the program, was still figuring out where I fit in, and yet was already being offered the chance to work on the product. This “great, want to build it?” philosophy was present throughout my internship here – I had a lot of flexibility and opportunity to build off of assigned tasks.
8. Would you come back to work at TechChange one day? Why?
Yes, and without a second thought. TechChange has to be one of the best work environments I’ve ever encountered; it’s fun and collaborative, the work is engaging, and the company is small enough that everyone can play a variety of roles. You might be hired as an educational technologist, but you’ll have the chance to do a little bit of graphics editing, write blog posts, sit in on business development meetings, teach a course, and have your voice featured in animations.
More importantly, this work has real value. The courses developed by TechChange are used by different organizations around the world to train staff members and health providers, as resources to newly-formed NGOs, and to put the spotlight on the role technology can play in the developing world. TechChange collaborates with organizations that work for real, sustainable change, and TechChange alumni go on to do incredible work. Being a part of this team has been a wonderful experience.
9. What advice would you give to future TechChange interns?
Take initiative! This is an awesome opportunity to grow your skill set – make use of that. If something needs to be done, volunteer to do it. Even if it’s not something you’ve done before, the team will support you and make sure you learn how to do it well. The TechChange team is also super supportive – if there’s something you want to learn about (even if it’s not directly related to your job), they’re more than happy to help.