As TechChange and our alumni community continue to grow, we’re sharing the stories of some of our rockstar alumni who have taken the tools they’ve learned and resources from their TechChange courses to make an impact. This week, we traveled to the OpenGov Hub to talk to FrontlineSMS Project Director Trevor Knoblich, who participated in our TC105: Mobiles for International Development course in March-April of 2012. Pursuing his interest in mobile technology in humanitarian response and journalism, Trevor combined his past background with his new connections and knowledge from TC105 to successfully land a job at FrontlineSMS.
Here is Trevor’s story, in his own words.
Why did you decide to take Mobiles for International Development?
Technology in humanitarian assistance was rare in back 2009. Back then, I remember how there was not yet much data sharing and effective data management between aid agencies. As a journalist working in humanitarian response, I became interested in how mobile technology could address various challenges throughout the world. Through my own research, I heard about different projects that involved data mapping and reporting of challenges with service delivery, such as infoasaid, but it was difficult to find a one-stop resource that gave me a good sense of emerging technology in humanitarian work. I wanted to know, what’s happening around the world? What tools are available for me to find out? And what tools are appropriate for my organization?
What was useful to you from TC105?
After doing a search on Google, I found TC105 and immediately enrolled in the course to get an overview of how mobile technology is being applied across international development. I found three key features of TC105 very valuable to me: the relevant information, the interactive experience, and the access to a network of experts in mobile tech.
- A central hub for the latest information for mobiles in development. TechChange’s TC105 became a central hub for emerging info and latest applications of mobile technology in the developing world. The TechChange team did a great job at selecting the most relevant and useful information for participants in the course by pulling all types of resources into one space. They included industry reports, real-world and current examples of tools like Magpi and FrontlineSMS, and practical case studies that inspired participants to try the tools out.
- Interaction, participation, and global dialogue. The unique interaction built into this TechChange course platform encouraged participation among my classmates. TechChange did a good job of getting participants to talk to each other with game mechanics. I liked the small size of the class that had ongoing global discussion forums (sometimes at 03:00 AM in certain places in the world) and incentives for me to stay actively engaged throughout the entire course. Live demonstrations of the mobile tools discussed in TC105 changed my perception and understanding of how some of those tools were actually used in real life.
- Access to a network of industry experts. TechChange invited and vetted an impressive lineup of global experts that presented for TC105. The “Live Event” discussion sessions were especially useful because real practitioners shared their anecdotes of the daily realities they face, and often shared industry resources such as website links and reports that sometimes are not yet on the course syllabus. For example, one of the speakers I remember most was Amy O’Donnell. She was representing FrontlineSMS and was extremely knowledgeable about community radio. In her discussion, she shared research papers and industry knowledge on best practices in the mobile tech space. Beyond these live video conference discussions, TechChange is always pushing for face to face connections when they can through alumni happy hours and a general open door policy.
How did TC105 ultimately impact you and your career?
Taking TC105 ended up being a smart career move. By keeping in touch with Amy O’Donnell, with whom I shared a common communications-oriented background, I eventually landed a job at FrontlineSMS as Project Director for the Knight Media Project. In this role, I manage grants and program design by connecting journalists with FrontlineSMS mobile technology for data management. It’s inspiring work, as I help journalists coordinate their staff, freelancers and citizen journalists, as well as reach out to a broader audience.
Advice from Trevor for taking TC105:
- Leverage TC105 within your own organization. If you’re advocating for your organization to adopt these new mobile tools and applications, you will have a variety of useful materials from TC105 to help make your case.
- Take TC105 first. Before taking any of the 200 or 300 level courses, TC105 gives you a good overview of emerging mobile technology and will help guide your selection for a deeper dive specific applications of mobile phones..
- Participate as much as you can. You’ll ultimately get more out of the course the more engaged you are with your classmates, the professionals who are presenting, and the TechChange staff.
About Trevor
Trevor joined FrontlineSMS in June 2012, and leads FrontlineSMS’ Knight Media Project. Prior to joining FrontlineSMS, Trevor worked as a humanitarian response coordinator with Lutheran World Relief, developing practices and protocols for emergency response in developing countries. His experience includes developing mapping and tracking systems for deployment of humanitarian aid. Before that, Trevor worked as a federal policy reporter in Washington, DC. His role allows him to combine his skills and experience in both international development and journalism. You can find him on Twitter @mobiletrevor.

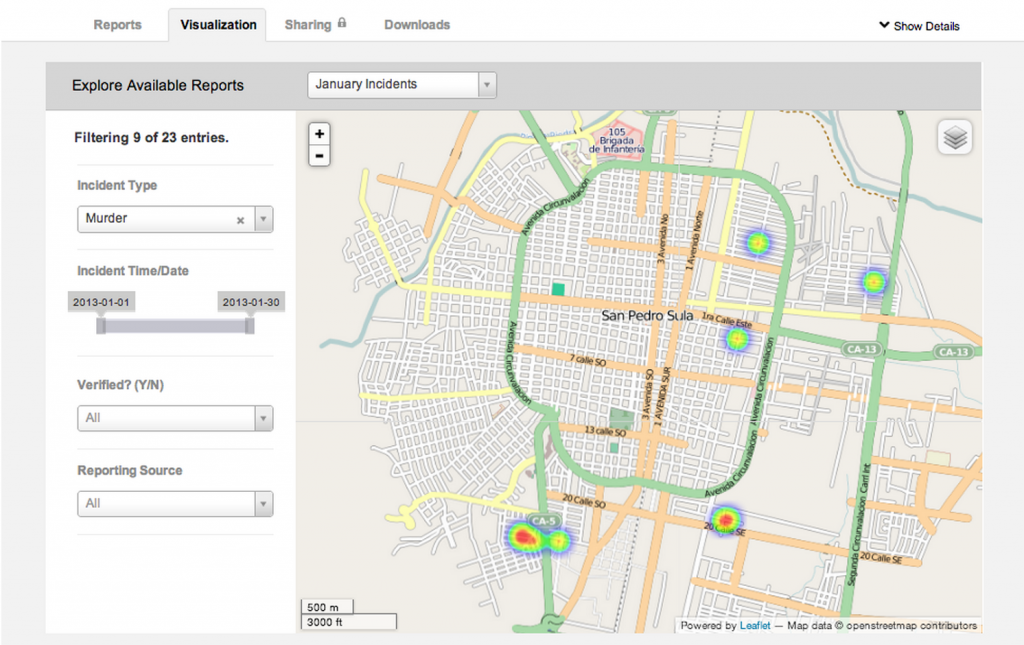
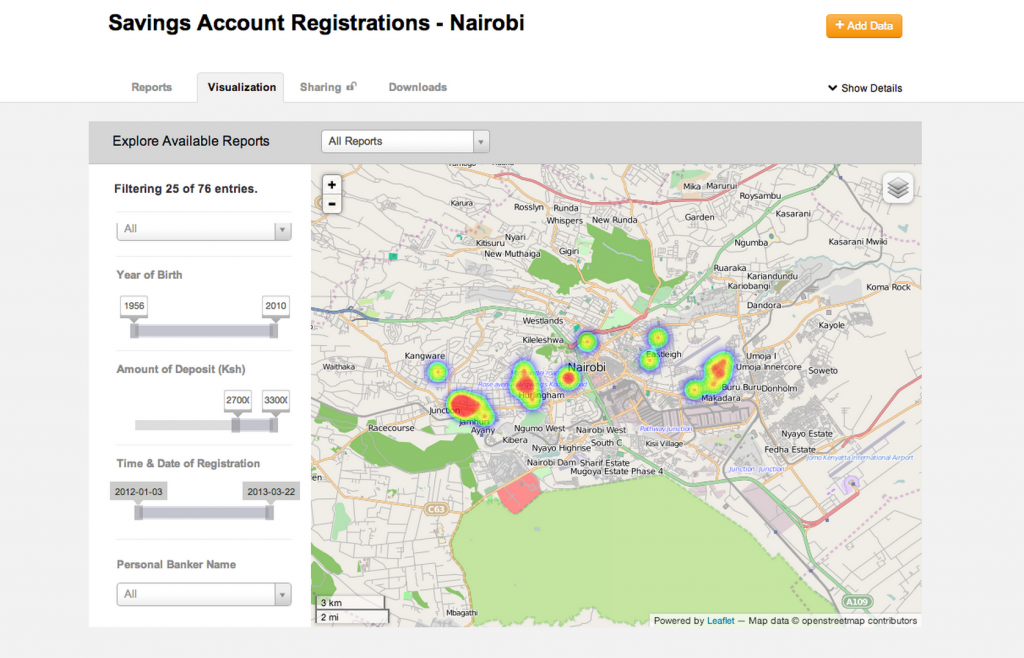
 The problem of preventing violence centers of two things; predicting where violence will occur and the ability for institutions to respond. Emmanuel Letouze, Patrick Meier and Patrick Vinck lay this problem out in their chapter on big data in the
The problem of preventing violence centers of two things; predicting where violence will occur and the ability for institutions to respond. Emmanuel Letouze, Patrick Meier and Patrick Vinck lay this problem out in their chapter on big data in the