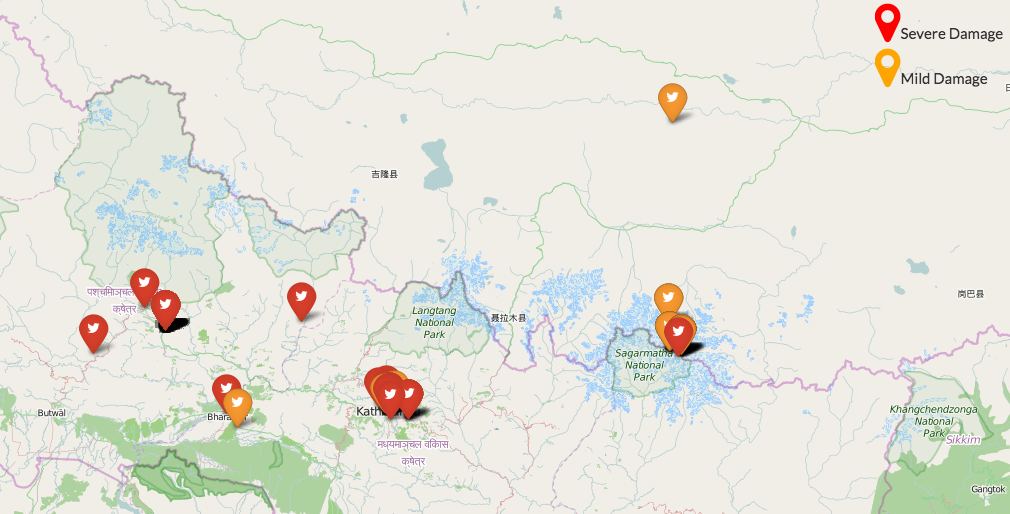
Did you see Facebook’s Safety Check feature recently? Did you use it?
Following the recent earthquake in Nepal, Facebook activated “Safety Check“, a feature that helps friends and relatives quickly find out whether their loved ones are safe. Safety Check was originally launched in October 2014 and was mainly based on experiences gained during the 2011 earthquake and Tsunami in Japan.
The idea is very simple: In case of a large scale emergency, Facebook can use the information it is constantly collecting about its users to determine who is likely to be in the affected area. It then asks these users to confirm whether they are safe and shares that information with their facebook friends. Alternatively, people can also report their facebook friends as being safe and those marked safe can see who marked them. People can also say “I’m not in the area”.
Safety Check is a dormant Facebook feature that is only activated when necessary. One thing that I had been curious about since the launch was how well Facebook would be able to determine whether someone was in the affected area.
According to the original press release:
“We’ll determine your location by looking at the city you have listed in your profile, your last location if you’ve opted in to the Nearby Friends product, and the city where you are using the internet.”
Indeed I quickly heard from two former colleagues who were in Nepal: One of them lives permanently in Kathmandu but was actually on a plane when the earthquake happened. In his case, Facebook assumed he was still in Nepal, because his phone was off at the time of the quake. In the absence of current information, Facebook took his home city and/or his last location, which was at the airport, to include him in the group of affected people.
The other person I know normally lives in the UK but was in Nepal on a trip. In his case, Facebook used the IP address of his last login to estimate his location.
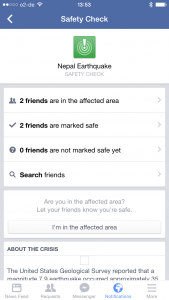
Users see how many of their Facebook friends are
in the affected area and how many are safe.
Why this is relevant
Anyone who has ever been in a situation where family members or close friends are in danger, knows that finding out what happened to them is one of the first things on your mind. Not knowing is not only a source of great anxiety, but it can actually be dangerous if you yourself are also close to the affected area:
Think of a father who knows that his daughter was at a shopping mall downtown when the earthquake struck. If he doesn’t know what happened to his child, he will probably run to the shopping mall to find out. By doing so he can put himself at risk and he will not be at home to look after the other children when a strong aftershock occurs. He will also try to call his daughter every 5 seconds, thereby accidentally helping to crash the phone network.
On the other hand, we have now seen in a number of disasters that internet connections frequently remain functional (if slow) even when phone and SMS networks are down – to a large part because many people open their WiFi networks to let others use the internet.
Using social media is also much more efficient since one “I am safe” update will reach all of one’s friends, making multiple calls unnecessary, thus reducing further load on the telecommunications infrastructure.
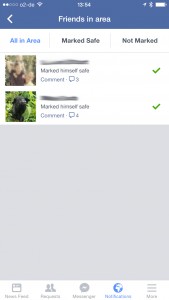
The application also shows clearly whether people have
reported themselves as safe or whether others have done so for them.
Why this is better
Of course, there are also other systems to find out whether friends and family are safe. Google, for example, has its “Person Finder“. The Red Cross Red Crescent Movement has been providing tracing and restoring family links services for many years and local government authorities, as well as embassies, are also very much involved in these tasks.
However all of them require that a (distressed) user finds out about these services and actively registers or gets in touch with them. That is a lot to ask of someone who just survived a disaster. Facebook’s Safety Check on the other hand is part of the normal Facebook application that most people are already familiar with. This reduces the barrier to share and receive information significantly which in turn reduces the load on the other, more sophisticated, systems like the Red Cross’ tracing program. Facebook’s Safety Check can provide clarity in many of the easy cases, freeing up resources for the difficult ones.
What do you think about Facebook’s Safety Check? Let us know by commenting below or tweeting at us @TechChange. This post originally appeared on Social Media 4 Good
Interested in learning about other ways technology is being used in disaster response? Join us in our upcoming online course on Technology for Disaster Response that begins on June 22.
About author

Timo Luege, TC103: Technology for Disaster Response Facilitator
After nearly ten years of working as a journalist (online, print and radio), Timo worked four years as a Senior Communications Officer for the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) in Geneva and Haiti. During this time, he also launched the IFRC’s social media activities and wrote the IFRC social media staff guidelines. He then worked as Protection Delegate for International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) in Liberia before starting to work as a consultant. His clients include UN agencies and NGOs. Among other things, he wrote the UNICEF “Social Media in Emergency Guidelines” and contributed to UNOCHA’s “Humanitarianism in the Network Age”. Over the last year, Timo advised UNHCR- and IFRC-led Shelter Clusters in Myanmar, Mali and most recently the Philippines on Communication and Advocacy. He blogs at Social Media for Good.