Have you seen our animations and wondered who is creating them? Meet one of our graphic designers who brings them to life, Rebecca Nelson.
Where are you from?
I am from Accokeek Maryland, which is not too far from DC so I know DC incredibly well, particularly when it comes to the museums.
What did you do before working at TechChange?
I worked as an Assistant Manager at Simulation Rides at the Smithsonian. I did some freelance projects on the side (customizing TOMS shoes for events at Nordstrom), but nothing I really wanted to, till I found TechChange.
How did you hear about TechChange?
I helped my friend apply to TechChange two or three years ago. He got the job and I got to watch the company grow from a third party perspective. I remember his job slowly developing from graphic designer, to motion graphics, to animation, then back down to illustration as he was able to specialize as the company grew. I was also able to see TechChange start from a room to an attic to where it is now and wanted to be a part of this incredible journey.
What exactly do you do at TechChange? What does a typical day look like for you?
Every day is different! Even though I mostly do character animation, it is a fraction of everything we work on here, so I have become more of a generalist, which has its own benefits. I have illustrated, done storyboards, recorded and cut audio, rigged assets, done motion graphics, designed 3D models, and then of course, animated.
I’ve really enjoyed getting to know every aspect of the pipeline, it has made me both more valuable as an individual who could make their own animations, and as a teammate able to know what the next person working on the same project needs.

Rebecca working on a project at her desk
How did you get into creative design?
Ever since I was little I loved the idea of animation, though as a child I had no idea what it was called, so I just drew a lot. I was much better at science or math, but I was fascinated by art because it was something I didn’t understand. Of course, now I know little things that help with design, like rule of thirds or that when the mind thinks of an object, it tends to be from a slightly above angle, because we usually have to look down on smaller items (an exception being things with screens, we tend to remember those from a straight angle).
What is the most important lesson you’ve learned working on animation projects for international development organizations?
It’s hard to boil it down to one single lesson. The first main thing I learned here was the pipeline of animation productions, even if it was as simple as a program shortcut. In animation lingo, I even started using a rigging system that allowed Inverse Kinematics (IK) on rigs in After Effects instead of Forward Kinematics (FK). It was a little bumpy at first because I learned the hard way the pivot points couldn’t be adjusted after the fact, but it was definitely valuable in the long run.
The second main thing I learned was the cultural and social aspects of animations. Clients usually want something very specific, and for good reasons. For example, characters must shake hands with the right hand because the left hand is considered disrespectful in certain cultures, and other specific requests like the relocation habits of refugees after a natural disaster. It’s fascinating to learn these as we work on these projects!
How do you keep up with the latest news in design?
My first source is my team at TechChange. Someone is always trying to innovate and streamline the design/production process. So, we naturally find out about new things in design. Second, I go to school in my spare time where I learn more about 3D modeling and rigging and texturing, which I have started to use at TechChange for small projects. Third, I watch a lot of cartoons. There’s a new generation of shows and content providers that allow a lot more independent and creator-based productions and the best way to learn about it is by just watching it.
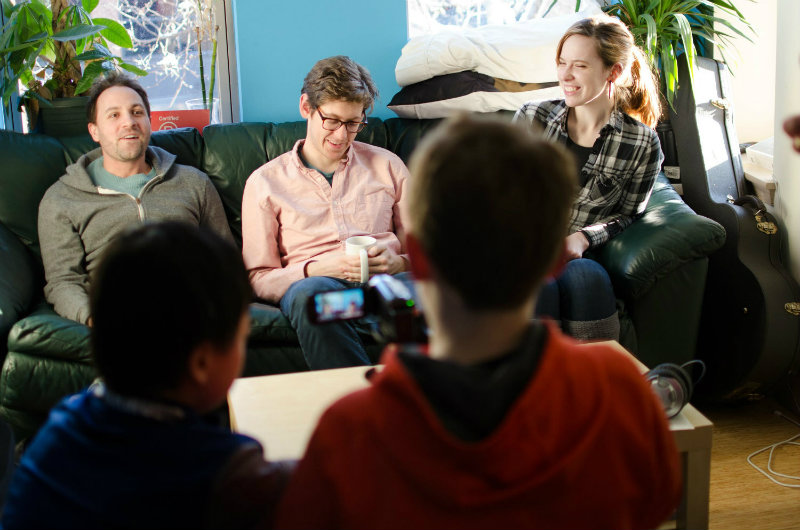

Dylan and Jack from Eastern Middle School in Silver Spring, MD interviewed Rebecca, Charlie, and Nick for a documentary on the 3D printers and prosthetics.
What do you love most about working at TechChange?
I love how open the company is. Everything is available to look at so there’s none of the bad things that one associates with big companies here. At any moment I can know what my higher ups are working on, where our energy comes from, what is going on with the courses, and I even know how much cereal is left because the cereal bar has clear containers!
What is your favorite TechChange moment so far?
I really love Show and Tell at TechChange. Every month, we do a team show and tell where we all get to show the rest of the team what we have been working on. I actually really hate presenting, but there’s nothing more beautiful than when people get to talk about something they’re passionate about. It goes back to my favorite thing about the TechChange, how transparent they are. I would never know about how hard everyone works if we did not take the time to highlight them. Oh, and we did wine and painting once as a group. It was a really interesting experiment seeing how each team member approaches the same challenge.
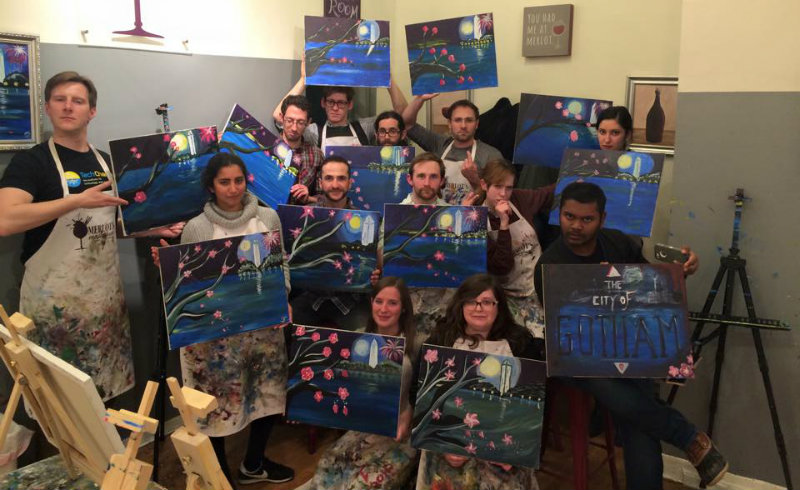

The TechChange team strikes a serious artist pose with their final art pieces during Wine and Painting night
What do you do when you’re not at TechChange?
I’m constantly taking some sort of class to get better at what I love, so I am mostly busy with homework. When I do finally decide to leave my home, I usually end up at a book store. My earliest jobs revolved around books; it’s a habit I never quite kicked.
If you had to direct someone to the best place to eat in D.C. where would it be?
U-street Cafe, since they combine both my love for breakfast food and peaches!