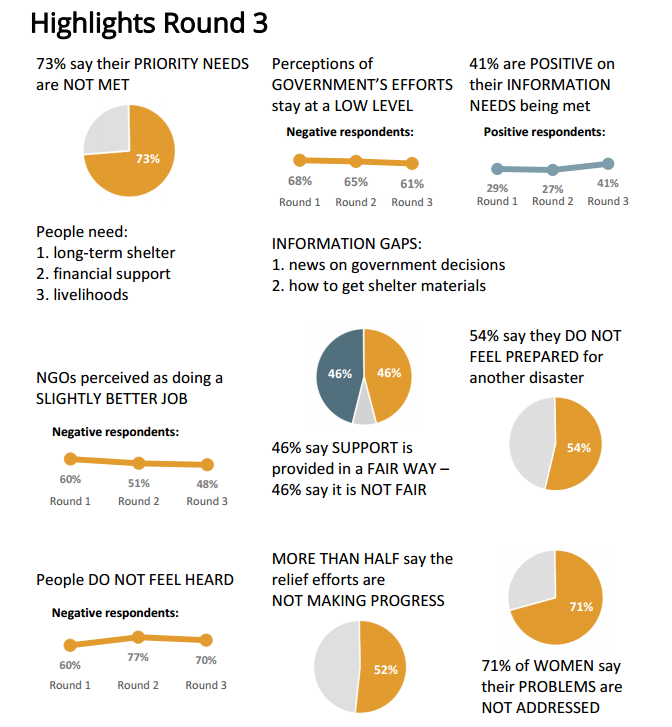
One of the things that sets the TechChange platform apart from other online courses is the network you are immersed in. Today, we are excited to highlight one of our alumna who took the network she built within one of our courses, into the incredible work she’s doing. Devjani joined us in our Technology for Monitoring and Evaluation course a few months ago, and her curiosity for the role of technology in M&E led her to take a deep dive in one of the tools she was introduced to in the course. We got to catch up with her on how the course has influenced her work.
How did you come across our Tech for M&E course?
I was on a year-long sabbatical in London from the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) in India. During my sabbatical, I wanted to learn more about the role of technology in monitoring and evaluation. I was looking for a course that would not only provide me a sound knowledge of the system but would also be cost-effective for me. So, after a few google searches, I came across TechChange’s course on Technology for Monitoring and Evaluation and immediately signed up!
Why were you curious about the role of tech in M&E?
NHPC’s power projects are located in far-flung villages, from Jammu and Kashmir in the North to Arunachal Pradesh and Manipur in the North-East. The project locations are very remote without any infrastructure, roads, or communication, making survey, investigation and project completion very challenging. Due to the remoteness of these projects, we have often noticed that the socio-economic surveys were not being conducted very diligently. We have often found that there are lot of discrepancies and inaccurate data collected on project-affected families during Social Impact Assessment Studies. Manual data collection in these remote villages has been cumbersome, and the staff have to carry GPS, cameras and papers into the field. Sometimes, the affected villages are so far out that it takes more than a day to reach it by foot, and in that case, the data collected in paper surveys are re-entered manually into Excel sheets, leading to a high margin of error.
After the manual collection of data, the monitoring is done through site visits (once or twice a year) and the data collected by external consultants doesn’t always reach the NHPC, making it difficult to have baseline information on the families affected by the project.
I knew there had to be a better way to collect data and do M&E!
How did TechChange provide you with the information you needed to make an impact?
In the TechChange course, I was introduced to so many possibilities of ICT in M&E, but I was hungry for more and wanted to take an even deeper dive. From the various M&E tools I got to know through the TechChange course, I was interested in learning more about a data collection tool, Akvo FLOW. I had attended a guest expert session with Marten Schoonman of Akvo, so I reached out to the course facilitator to help me get in touch with him. Marten put me in touch with the Akvo India group and I was able to attend a five-day training session in India with the Akvo team to learn all about the tool and how well I can use it in my organization.
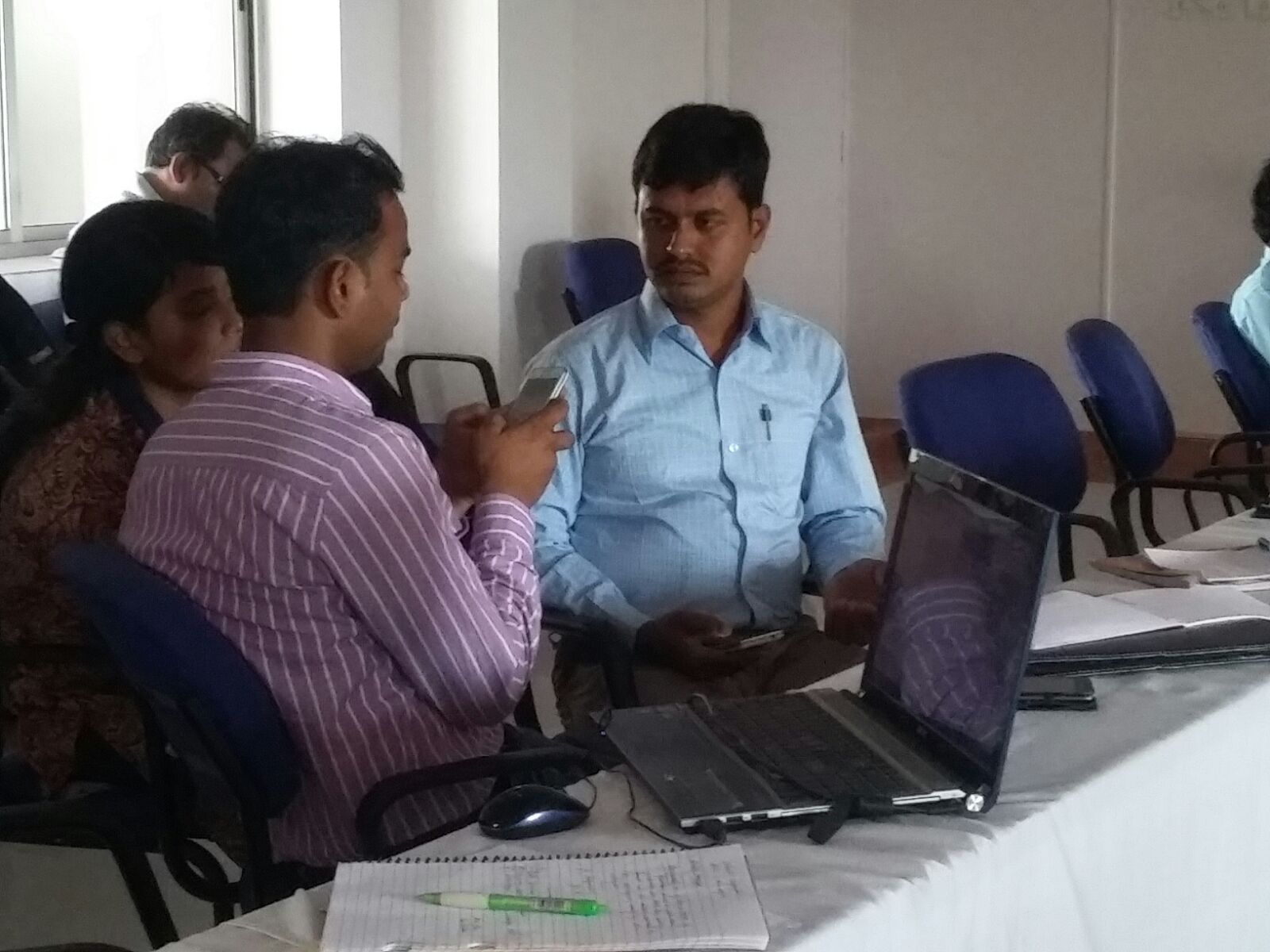

Picture from the Akvo FLOW training in India
I attended a 5-day training, organised by the India chapter of the Akvo group with 40 other attendees. Everyone came from diverse backgrounds; some were tech savvy and highly educated while others were handling smartphones for the first time. It was a great opportunity for me to really dive into one specific tool that I was curious about.
Tell us more about Akvo FLOW
Akvo FLOW is a data collection platform that is used on inexpensive mobile phones with an Android platform. It has helped me with all of the following:
- Getting the GPS coordinates
- Obtaining authentic data from inaccessible respondents
- Surveying a greater geographical area at lower costs
- Ease of obtaining data on the dashboard
- Using it in areas where there is no mobile network
- Managing a database of respondents who can provide loads of data that can be used for baseline studies and longitudinal impact assessments
- Geo-mapping of sampled areas and use of media such as pictures, audio and video,
- Creation of identity cards
- Data analysis and evaluation
Since NHPC’s projects are located in remote areas all over India, we can use Akvo FLOW to collect data from all projects in a standardised format and have it all in the same platform.
Any advice for someone considering a TechChange course to break into the ICT4D field?
Today, ICT has become an indispensable tool to bridge distances and spread the seeds of development in the remotest corners of this world. For funders and development workers, monitoring in remote areas is a daunting task, but the expansion of ICT has now paved the path towards limitless possibilities, providing easy access to information to make informed decisions. ICT4D is not just about computers, mobile phones and the internet, but it is also about help, support and capacity building of people who are using them and linking them with the right communities.
Here are five reasons I would always recommend TechChange courses:
- Extremely helpful and cooperative course coordinators. I was totally new to ICT when I enrolled for this programme, so I was prepared to feel lost. But with the help of facilitators and guest experts, I could get hands-on experience with the Akvo FLOW tool. This has opened a new door of opportunity for me and I am excited to implement what I learned to my work.
- Course material is beyond just PowerPoints. It’s very interactive with plenty of networking opportunities, group discussions and presentations, live question and answer sessions, feedback from other participants, video chats, etc. making the whole learning process very engaging and enjoyable. There is plenty of learning opportunities from course participants as well, who are very experienced and coming from different parts of the world with different sets of skills and approaches.
- Courses are very well crafted and exhaustive yet comprehensive. Excellent study materials that are up to date.
- Connecting with guest experts who are leaders in the ICT4D industry. It’s very difficult to get access to such a range of good study materials and get to hear from the experts themselves.
- Courses are easily accessible. All the course material, even live events are recorded and archived for those who could not attend the live sessions. Then, the course materials are available even 4 months after a course ends, which gave me ample time to catch up and get a grasp of the whole syllabus.
What’s next?
It is going to be a daunting task to introduce ICTs in our public sector, but I am going to take up brainstorming sessions with senior officers from various organisations and try to understand how to effectively use these tools in our crucial surveys and monitoring of community development and CSR programmes and also use the same for conducting Social Impact Assessment studies.
“Nothing stops an organization faster than people who believe that the way they worked yesterday is the best way to work tomorrow. To succeed, not only do your people have to change the way they act, they have got to change the way they think about the past.” – Former Chairman of KPMG International, Jon Madonna.
So my journey begins here. I know it’s an uphill task to convince the system to accept this Akvo FLOW tool, which opens a whole new world of data transparency and authenticity, and successfully integrating the tool in our various development programmes.
I would really like to thank the whole TechChange Team for giving me this opportunity to share my views and experience with you all. I am going to come back to them over and over for many more courses that would not only ensure progress in my professional development but also give me inspiration and satisfaction to work successfully in the field of social development.
***
Interested in learning more about data collection, you can still join our Tech for Data Collection and Survey Design course that started on Monday! Want a more immersive experience? Check out our Tech for M&E Diploma program!
About Devjani

Devjani has been working for over 18 years in India with a successful track record in the area of Environment, Social Development, CSR and Sustainability. Her experience extends across large hydro and mining projects within the government & NGO sectors and international funding agencies. She has travelled extensively in India to conduct a range of investigative studies. Devjani is a Registered PRINCE2 Practitioner and has a postgraduate degree in Public Systems Management with specialisation in Environment. She has also done a Post Graduate Certificate course in Environmental Impact & Assessment with specialisation in Strategic Environment Assessment.
Featured image: Isha Parihar from Akvo India trying to calibrate the GPS in the field