Text to Change’s Chief Technology Officer, Marcus Wagenaar, sat down with me yesterday to discuss new projects on the horizon and innovations in the mHealth field. Text to Change is an international NGO which uses technology for social change, or as Marcus puts it, “not just a tech company.” Instead, outreach is where Text to Change works. As the knowledge bearers about mHealth systems and needs, they help design, conceptualize, manage and analyze outreach and projects with their implementing partners to address gaps in healthcare systems and information.
Text to Change’s Chief Technology Officer, Marcus Wagenaar, sat down with me yesterday to discuss new projects on the horizon and innovations in the mHealth field. Text to Change is an international NGO which uses technology for social change, or as Marcus puts it, “not just a tech company.” Instead, outreach is where Text to Change works. As the knowledge bearers about mHealth systems and needs, they help design, conceptualize, manage and analyze outreach and projects with their implementing partners to address gaps in healthcare systems and information.
I asked Marcus to talk a bit about some of his favorite projects:
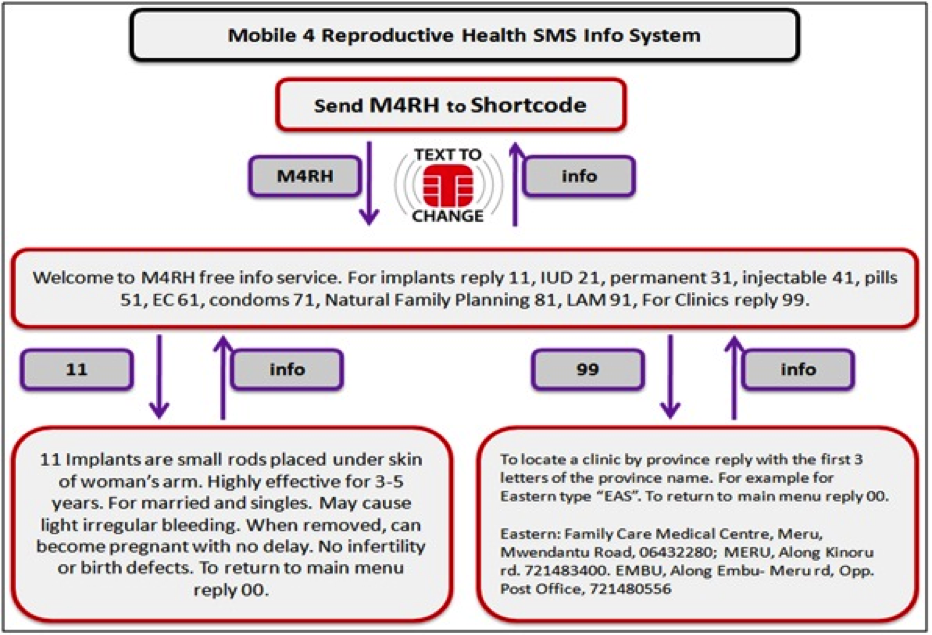
Mobiles for Reproductive Health (m4rh), in collaboration with FHI, uses SMS and web based software to send targeted messages about reproductive health. The user gets their first message and is given 1-3 options for response, such as “if you want more information about condoms, text back 001.” They are then inside a tree of responses win which they can navigate back and forth and discover new information. The project has been running in Kenya and Tanzania for over a year with pilots in Ghana and Rwanda underway. FHI provides the content and updates, Text to Change runs the IT backend in each country, all from Kampala.
m4rh is one of Marcus’ favorites because it’s “inherently scalable, once it’s set up anyone can access it for free by texting the first keyword to get the main menu” and it’s the “perfect example of Text to -Change because it provides people with information to make informed choices about their lives. In situations where information is lacking or inaccurate around sensitive issues of reproductive health, m4rh allows people to access information that can give them more control over their lives. They still make their own decisions but at least they have all necessary information to make an informed choice.”
As example of its popularity; in May 2012 more than 40 thousand people have accessed the M4RH information service in Kenya alone. The specific information people access in the system is analyzed. Also, SMS surveys amongst users are carried out to enable deeper analysis of behavioral patterns. By combining this information various things can be deduced. Examples are: which contraceptives are popular in which age groups, what are the differences in male and female use of the system, are the choices people make influenced by the system, etc. These research results or not yet in the public domain but have been shared at various mHealth conferences and we hope to be able to share the results with a wider audience in the near future.
The Medical Male Circumcision project, in partnership with Jhpiego in Tanzania and potentially Uganda, is a service hat sends information, similar to m4rh, as well as supporting patient recovery. Individuals in the beneficiary population get messages regarding where they can receive Medical Male Circumcision and why it’s important, such as “Male circumcision can reduce the risk of female-to-male HIV transmission by 60%”. After surgery, patients receive messages as soon as the surgery is complete regarding what to expect during their recovery. The Medical Male Circumcision project provides a Virtual Nurse who advises patients: “Make sure that you do not have sex for the first two days,” for example, or later on in the recovery “if your urine is discolored, visit the clinic.” The messages are “specific but lighthearted” with quiz questions every week to engage the patients and to assess how much they know about Medical Male Circumcision. Messages are meant to be encouraging and a “positive way to ensure recovery,” reduce stress, and “decrease health costs overall” by addressing concerns before they become serious health issues.
Text to Change monitors how many people they reach with their messages, how often they are reached, and how much it costs to reach a person. Researchers were able to show a statistically significant association between those men who texted in to the toll-free number asking where male circumcision was available and those who actually followed through and got circumcised. This is a good example of providing people with information to help them making informed decisions about their own health.
Data Collection
The data collection project is in the pilot phase with the Center for Disease Control in Tanzania within the mHealth Alliance. The project targets mothers after they have delivered and will speed up data collection about Vertical or Mother-to-Child-Transmission (MTCT) of HIV. Currently, midwives and nurses fill in registers for mothers and babies to track their data by hand. The individual patient data is rarely analyzed and often inaccessible to researchers and government representatives so that today there is no reliable number for the transmission rate for MTCT in Tanzania. This Data Collection tool pilots a new form for tracking MTCT data, where healthcare workers take data from the standard register, write it on a worksheet and then copy it line by line and send it to a central location using SMS. The data collected will allow the CDC to calculate the transmission rate for the first time in Tanzania and will enable impact evaluation of interventions that aim to lower the number of Mother to Child Transmission of HI, which is part of the Millennium Development Goals.
I also asked Marcus to give a window into exciting innovations in the pipeline:
FormHub is an Open Source initiative by Columbia University. Text to Change is working with Columbia to develop and use their platform in the field. Text to Change is currently implementing this technology with one of their partners. The partner will conduct a survey in Uganda’s Luwero District, interviewing 1000s of teachers and students in secondary school about physical abuse, sexual abuse, living conditions, and emotional and physical wellbeing of children. This is the first ever large-scale survey about these sensitive issues performed in Uganda. The partner designs the survey questions, Text to Change enables easy data collection using mobile technology and the formhub platform. Using cheap Android phones, 60 trained Ugandans will carry out the survey using FormHub.
Marcus also wants to use FormHub to automate data gathering in health and medical setting in remote clinics because it’s simple to use for the designer, data collector and data analist and it’s open source. Many more interesting projects to come!
Vusion is a new SMS open source platform development by Text to Change. The backend is based on the Vumi system developed by the Praekelt Foundation. Marcus sees Vusion as the next big thing in SMS messaging, and here’s why:
- Vusion is focused on providing a scalable enterprise messaging platform
- It can connects to multiple telecom companies and aggregators in multiple countries and multiple shortcodes
- Once Vusion is set up, you won’t need a programmer to design campaigns or access data so it’s easy for non-technical project managers to use without programming skills
- An API enables access to SMS data from external applications, which enables easy development of for example; advanced real-time data visualizations, website-widgets, twitter integration, etc.
- Vusion has different access levels and enables organizations to implement and manage multiple SMS programs in parallel from one central platform.
Programmer? You can download Vusion from github and see what the skeleton looks like.
Some of the cost implications of SMS projects are annual dedicated shortcode fees and aggregator costs. Vusion reduces this by enabling shortcode sharing. Users can use the same shortcode for small projects to share infrastructure and still be in full control over their campagins and projects This is the approach Text to Change has been pioneering for years but Vusion will make it easier for organizations to be more involved in their own campaigns by having full access to their projects and the associated data.
Vusion was launched with an extensive demo on the 15th of June in Amsterdam. There is no recording of real-live demo but an accompanying presentation is available on slideshare.
Interested in learning about Mobiles for International Development? Check out our upcoming course, mHealth: Mobile Phones for Public Health, starting in November.