Some 85 percent of the world population has access to Internet nowadays. An increasing number of users venture online with a mobile device – smartphone or tablet – rather than with a PC. About 25 percent of the world population uses social media, while three-quarters of the online population uses one or more social networking sites. Around the world, there are some 1.28 billion Facebook users, with 540 million on YouTube, 187 million on LinkedIn, and 255 million on Twitter. (Source: Brief History of Social Media)
The unprecedented pace of technological advance over the past years, gave millions of people around the world the opportunity to use internet, social media platforms and mobile phones not just to consume information but also to produce it. The increasing sense of empowerment that social media lends its users, regardless of where and who they are, has led to a number of “social media revolutions” credited with toppling governments and totalitarian regimes around the world.
The Arab Spring is often heralded as one of history’s biggest social media victories. This wave of protests began in December 2010 and proceeded through 2011 as rulers were forced from power in Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, and Yemen, and protests broke out in other countries in the region, including in Bahrain, Syria, Algeria, Iraq and Jordan, to name just a few. While there was no cohesive campaign or strategy at grassroots level, social media played a crucial role during this time, allowing individuals to organise themselves, communicate and voice their complaints publicly. Many contributed to the virtual protests as well as the physical ones through the use of social media. Combined, these efforts caused governments to take notice.
The Internet and new technologies are increasingly influencing not only the way people respond to and recover from conflicts, but also the way they further engage in conflict transformation and peacebuilding. Part of creating communities that can advance peacebuilding is harnessing the power of technology to bring people together, promote conflict management and resolution, and create the public will to change attitudes and behaviours.
New tools for monitoring violence, sustaining dialogue during peace processes, and localising peacebuilding efforts have emerged in recent years as access to mobile phones and internet has increased worldwide. The outreach of these tools goes well beyond the conflict resolution expert circle, enabling people around the globe to share first-hand witness reports of violence, social unrest, human rights infringements, election fraud, political instability, etc. and become agents of change within their own communities. This collaborative approach is known as ‘crowdsourcing’ (i.e. crowd + outsourcing).
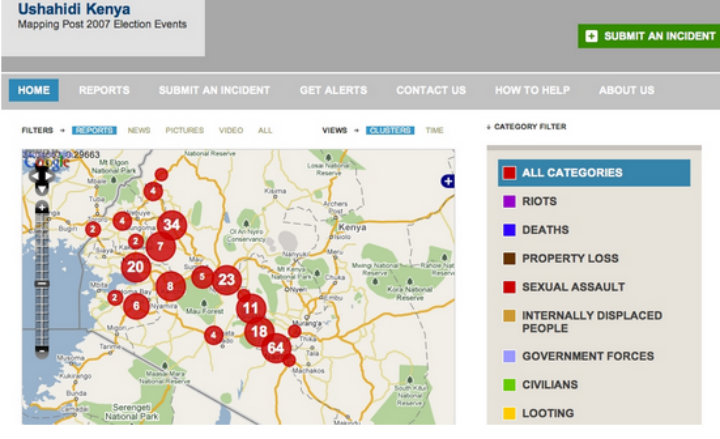
In early 2008, in the midst of post-election violence, Kenyans have for the first time used the Ushahidi open-source platform (Ushahidi is the Swahili term for ‘witness’ or ‘testimony’) to collect, visualise and interactively map eyewitness accounts of violence incidents (which would have otherwise remained largely unreported by media, government or police).
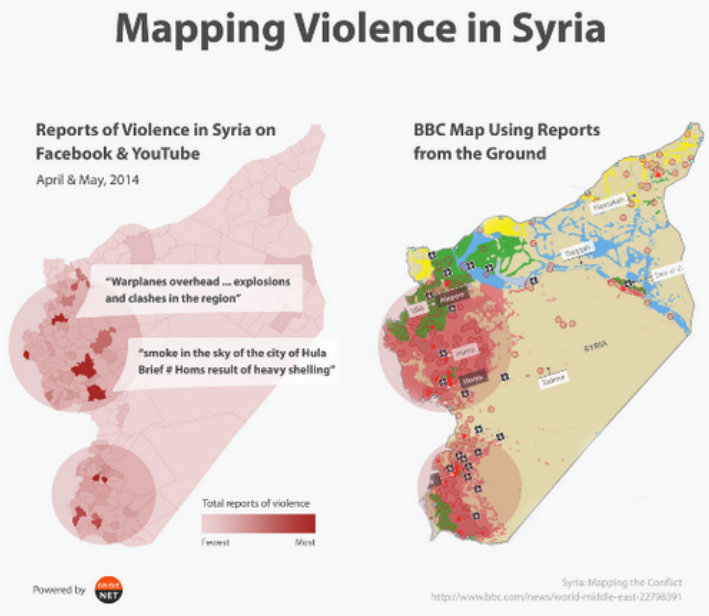
The Syria Tracker Crisis Map is another impressive crowdsourcing effort launched shortly after the protests began, in April 2011, to collect citizen reports on human rights violations and casualties. Combining automated data mining and crowdsourced human intelligence, the Syria Tracker provides a continually updated list of eyewitness reports from within Syria, often accompanied by media links; aggregate reports including analysis and visualisations of deaths and atrocities in Syria; as well as a stream of content-filtered media from news, social media (Twitter and Facebook) and official sources. This approach could provide a powerful means to assess the human cost of war in Syria.
CrisisNET is another tool which harnesses ‘big data’ coming from social media to map violence. Their Syria mapping is as accurate as the one BBC did with reporters on the ground.
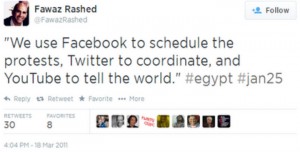
There are several ways in which today’s social media can be leveraged to prevent and manage conflict. Early warning is critical for early response. Permanent conflict monitoring for real-time awareness can help inform appropriate and timely interventions. Likewise, social media can provide real-time feedback on what works and what doesn’t, thus serving as a complementary channel of information for impact evaluation. Finally, as the Arab Spring mobilisation has clearly shown, social media can facilitate self-organisation for early response. Needless to say, the capacity to self-organise also renders conflict prevention networks more resilient. In other words, social media can be used to power civil resistance in nonviolent movements that seek to end oppression and bloodshed. As one Egyptian activist reported during the revolution, “We use Facebook to schedule the protests, Twitter to coordinate, and YouTube to tell the world.” Social media can be similarly leveraged to facilitate a resilient people-centered approach to conflict prevention.
This post originally appeared on Pax Christi International.
About Ramona Kundt
Ramona Kundt is a Brussels-based communications professional working with Pax Christi International, a network of peacebuilding NGOs. Her work is focused on advocacy, campaigning and communications coordination on issues pertaining human rights, human security, disarmament, religion and violent conflict. An alumna of TechChange online courses in Social Media for Social Change and Technology for Conflict Management and Peacebuilding, she is particularly interested in how social media can influence the way people respond to conflicts, and engage in conflict transformation and peacebuilding, for a lasting positive social change. She has volunteered with various humanitarian and development projects in Africa, most recently in the Maai Mahiu Internally Displaced Persons Camp, in Kenya.