The following is a guest post by Christian Douglass, a TechChange alumni from TC104: Digital Organizing and Open Government.
What makes the Open Government Partnership – seemingly another multilateral good governance initiative — worth watching?
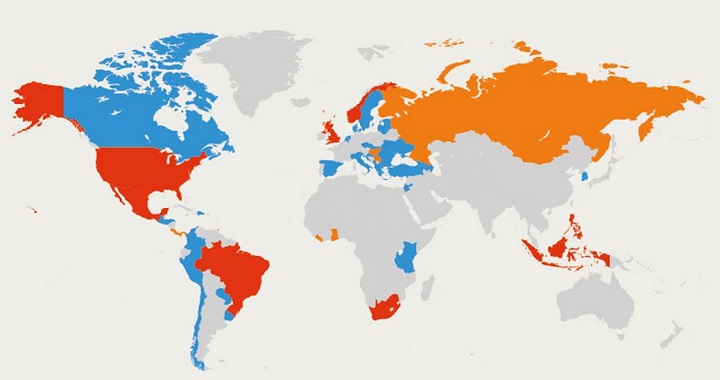
It’s not because it’s grown from eight to fifty-eight countries in under two years. That’s fast, and fifty-eight is a respectable number – it demonstrates momentum – but plenty of multilaterals, like the Community of Democracies, reach that number early on.
The Open Government Partnership (OGP) is President Obama’s international expression of his pledge to make his administration the most transparent in U.S. History: In November 2012, after a trip to all-the-reform-rage country of Burma, President Obama secured a commitment from the once international pariah to work towards OGP eligibility by 2016. Time will tell if the cadre of former generals will meet that tall order, but they have showed a willingness to try. The international community, including the U.S., is bending over backwards to help.
President Obama also made the OGP a top-line message in a recent Oval office visit by four African heads of state. As a carrot for being democratically elected governments, Cape Verde, Malawi, Sierra Leone, and Senegal were invited to the U.S. in March. Those that were OGP eligible, such as Cape Verde and Malawi, committed to join. Sierra Leone pledged to work towards eligibility. A rule of thumb: If the President mentions anything twice, the bureaucracy takes notice. As a result of the visit, don’t expect OGP to be taken out of talking points until the next election cycle.
But there are two really good reasons to watch the OGP:
First, the role of civil society. One of three co-chairs is a CSO, as well has half of the 18-member steering committee. Additionally, countries are required to form, track, and review commitments in conjunction with civil society during the action plan lifecycle. Governments have to develop commitments in conjunction with local civil society stakeholders, as well consult with the OGP steering committee before finalizing their commitments. This is no panacea, but it represents a very significant opportunity for civil society.
Secondly, the OGP is action –not talk – driven: the first eight country self-assessment reports on action plans are being publically published in the next several months. An independent third-party will review the progress of the action plans and publish their findings by October. Thus, 2013 is a big year for the OGP. If it is too maintain momentum and solidify legitimacy, the independent assessment process has to produce credible reports of each country’s accomplishments for public review.
And here is why the OGP might be different: Countries develop their open governance projects, as long as they fall within the parameters of the OGP five “grand challenges” that focus on the four OGP principles: Transparency, Citizen Participation, Accountability, and Technological Innovation.
For example, as a part of their OGP commitment, Mongolia recently announced they have instituted electronic balloting, removing another opportunity for voting officials to influence the outcome – which can slowly build trust in governing institutions. Brazil recently instituted “clean slate” laws: No official may have a criminal record. This may sound baseline and intuitive, but after the law was passed it was revealed that many officials had records.
Each country designs and owns which handful of projects they launch. In this way, the good governance accomplishments of OGP partner countries might be like the tenure of former Secretary of State Clinton.
Secretary Clinton did not choose one big “legacy” accomplishment, like advancing Middle East peace. Instead, like a good venture capitalist, the State Department, under her guidance, seeded projects around the globe as diverse as promoting better cook stoves in Asia to battling human trafficking in India. She had her theme of “economic statecraft,” but what that meant in each country was context specific.
The Open Government Partnership, if it is to be deemed successful, may be measured in that same way: A thousand local good governance developments all adding up to something big and continuous. In that way, it is very much an initiative for the Internet Age, where a thousand voices in Egypt can start something that can’t be bottled up.