By Timo Luege, TC103: Tech Tools and Skills for Emergency Management facilitator
As Ebola continues to ravage Sierra Leone, Guinea and Liberia, people from all around the world are working together to stop the disease. In addition to the life saving work of medical staff, logisticians and community organizers, information and communication technology (ICT) is also playing a vital part in supporting their work.
After consulting the TechChange Alumni community and other experts in international development and humanitarian assistance, I pulled together a list of different technologies being applied to manage Ebola. Below are six examples showing how ICT is already making a difference in the current crisis.
1. Tracing outbreaks with mapping and geolocation
Aside from isolating patients in a safe environment, one of the biggest challenges in the Ebola response is tracing all contacts that an infected person has been in touch with. While that is difficult enough in developed countries, imagine how much more difficult it is in countries where you don’t know the names of many of the villages. It’s not very helpful if someone tells you “I come from Bendou” if you don’t know how many villages with that name exist nor where they are. The Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team has helped this process through creating maps since the beginning of the response.
See: West Africa Ebola Outbreak – Six months of sustained efforts by the OpenStreetMap community.
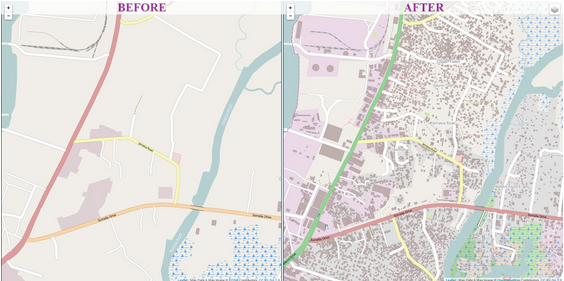
Map of Monrovia in OpenStreetMap before and after volunteers mapped the city in response to the Ebola crisis. (Humanitarian OpenStreetMap)
In addition, the Standby Task Force is supporting the response by helping to collect, clean and verify data about health facilities in the affected countries. The information will then be published on UN OCHA’s new platform for sharing of humanitarian data.
2. Gathering Ebola information with digital data collection forms
Contact tracing involves interviewing a lot of people and in most cases that means writing information down on paper which then has to be entered into a computer. That process is both slow and prone to errors. According to this Forbes article, US based Magpi, who just won a Kopernik award, is helping organizations working in the Ebola response to replace their paper forms with digital forms that enumerators can fill out using their phones.
Digital forms not only save time and prevent errors when transcribing information, well designed digital forms also contain simple error checking routines such as “you can’t be older than 100 years”.
If you are interested in digital forms, check out the free and open source Kobo Toolbox.
3. Connecting the sick with their relatives using local Wi-Fi networks
Elaine Burroughs, a Save the Children staff member who is also TechChange alumna of Mobiles for International Development, shared that they are using their local Wi-Fi network to connect patients in the isolation ward with the relatives through video calls. Both computers have to be within the same network because local internet connections are too slow. In situations where video calls are not possible, they provide patients with cheap mobile phones so that they can talk with their relatives that way. Elaine added: “Several survivors have told us that what kept them going was being able to speak with their family and not feel so isolated when surrounded by people in hazmat suits.”
4. Sharing and receiving Ebola information via SMS text messages
I have heard about a number of different SMS systems that are currently being set up. Some are mainly to share information, others also to receive information.
mHero is an SMS system specifically designed to share information with health workers. It works with UNICEF’s RapidPro system, a white label version of Kigali-based TextIt which is one of the best SMS communication systems I know. RapidPro is also at the heart of a two-way communication system that is currently being set up by UNICEF, Plan International, and the Scouts.
The IFRC is of course using TERA to share SMS, a system that was developed in Haiti after the 2010 earthquake and already used in Sierra Leone during a recent cholera outbreak.
5. Mythbusting for diaspora communities via social media
Social media also has a place, though not as much as some people think. With internet penetration at less than 5 per cent in Liberia and less than 2 per cent in Sierra Leone and Guinea, it is simply not relevant for most people – unlike radio for example. However, all of these countries have huge diasporas. The Liberian diaspora in the US alone is thought to be as many as 450,000 people strong – and they all have access to social media. Experiences from Haiti and the Philippines show that the diaspora is an important information channel for the people living in affected countries. Very often they assume that their relatives in the US or Europe will know more, not least because many don’t trust their own governments to tell the truth.
Social media can play an important role in correcting misinformation and indeed, both the WHO and the CDC are using their social media channels in this way.
6. Supporting translations of Ebola information remotely online
Last but not least, Translators Without Borders is helping NGOs remotely from all over the world to translate posters into local languages.
Low tech does it
As a final word, I’d like to add that while technology can make a real difference we must not forget that very often low tech solutions will be more efficient than high tech solutions – it depends on what is more appropriate for the context. So don’t start an SMS campaign or launch a drone just because you can. It’s not about what you want to do. It’s not about technology. It’s about what’s best for the people we are there to help.
We will be discussing these technology tools, Ebola, and many similar issues in TC103: Tech Tools and Skills for Emergency Management and TC103: mHealth – Mobiles for Public Health. Register by October 31 and save $50 off each of these courses.
Do you have additional examples of how ICT is helping in the Ebola response? Please share them in the comments!
This post originally appeared in Social Media for Good.
About the TC103 facilitator: Timo Luege
After nearly ten years of working as a journalist (online, print and radio), Timo worked four years as a Senior Communications Officer for the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) in Geneva and Haiti. During this time he also launched the IFRC’s social media activities and wrote the IFRC social media staff guidelines. He then worked as Protection Delegate for International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) in Liberia before starting to work as a consultant. His clients include UN agencies and NGOs. Among other things, he wrote the UNICEF “Social Media in Emergency Guidelines” and contributed to UNOCHA’s “Humanitarianism in the Network Age”. Over the last year, Timo advised UNHCR- and IFRC-led Shelter Clusters in Myanmar, Mali and most recently the Philippines on Communication and Advocacy. He blogs at Social Media for Good and is the facilitator for the TechChange online course, “Tech Tools & Skills for Emergency Management“.